WeatherControl

This project uses Wissance.WebApiToolkit so please give us a star! And for this project too!
1. General description
This project from the one side is a tutorial about how to design REST API using C#, but from the other side it is also fully functional Web API (REST) for working with meteorological stations or with indoor conditions sensors.
REST APIwithEntityFrameworkORM-Wissance.WeatherControl.WebApiprojectREST APIwithEdgeDbGraph DB-Wissance.WeatherControl.WebApi.V2project
These 2 Project previously having had (< 2.0) different data Model, but starting from 2.0 they have the same data model.
These projects targets multiple platforms - netcore 3.1, net6 and net8.
2. Data Model
2.1 Glossary / Domain object
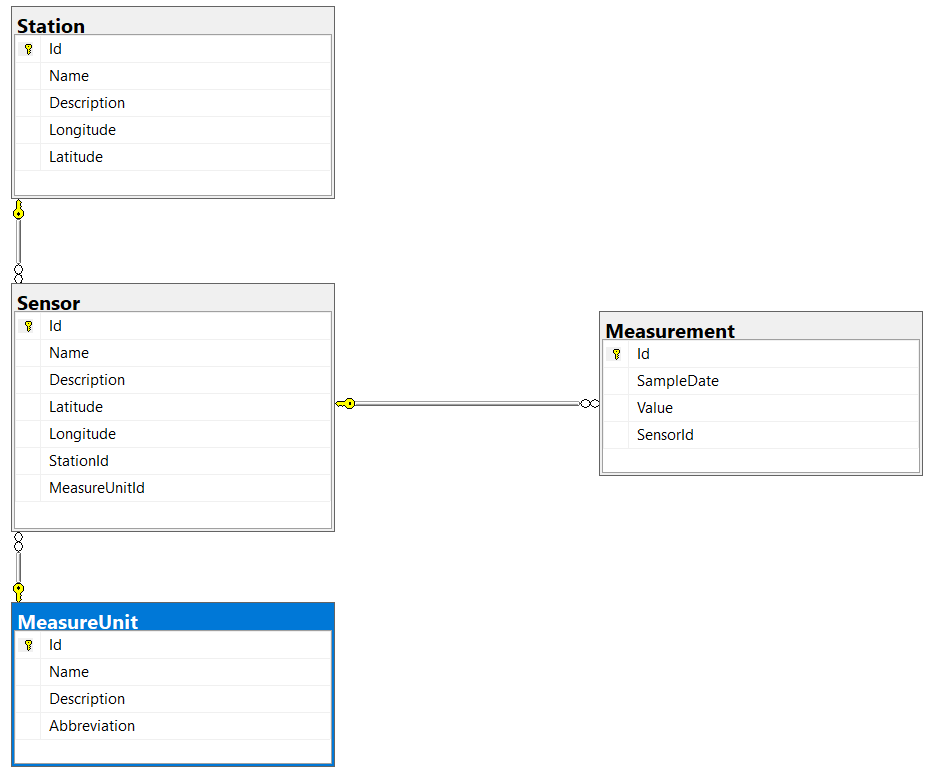
Station- weather station that has name, description, coordinates and it can collect and store any number of parameters, 1 measuring parameter - 1Sensor;Sensor- sensor that measures physical values likeTemparature,Pressure,Humidityand so on, 1 sensor measures only one 1 physical value;MeasureUnit- physical value itself that is measuring bySensor.Measurement- Sensor values = timestamp + numeric (decimal) value.
3. REST API With Entity Framework
3.1 Application Overview
Web API (REST) service (.Net Core) could store weather data from multiple weather station with multiple (any number) sensors, typically meteo stations store/manage following physical value measurements getting from appropriate sensors:
temperature;atmosphere pressure;humidity;wind speed;
Application has 4 resources = Domain objects
Application uses MsSql (Sql Server) as Database Server (this could be easily changed, but this required to re-generate migration).
StationSensorMeasureUnitMeasurement
Here is relations between objects in SQL database:
3.2 Overall usage scenario
This is a very simple application (demo), if any feature is needed open new issue/request. Every REST resource described in a separate sub chapter.
3.2.1 Operation with MeasureUnit resource
First we should configure what we would like to measure, we could do it via POST ~/api/MeasureUnit with body i.e.:
{
"name": "Wind speed",
"description": "",
"abbreviation": "V, mm/s"
}
curl -X 'POST' \
'http://127.0.0.1:8058/api/MeasureUnit' \
-H 'accept: text/plain' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"name": "Wind speed",
"description": "",
"abbreviation": "V, mm/s"
}'
We could edit created MeasureUnit via PUT ~/api/MeasureUnit/{id}, with new body, i.e.:
{
"name": "Wind speed",
"description": "Wind speed in mm/s",
"abbreviation": "V, mm/s"
}
curl -X 'PUT' \
'http://127.0.0.1:8058/api/MeasureUnit/b23b25dc-49df-42e3-8374-08dcf37af278' \
-H 'accept: text/plain' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"name": "Wind speed",
"description": "Wind speed in mm/s",
"abbreviation": "V, mm/s"
}'
Or get multiple objects - GET ~/api/MeasureUnit
3.2.2 Operations with Station resource
- Create Station:
POST http://localhost:8058/api/station
{
"name": "Ufa meteo station",
"description": "Meteo station in Ufa city",
"longitude": "55°96'0\"E",
"latitude": "54°7'0\"N",
"sensors": []
}
curl -X 'POST' \
'http://127.0.0.1:8058/api/Station' \
-H 'accept: text/plain' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"name": "Ufa meteo station",
"description": "Meteo station in Ufa city",
"longitude": "55°96'\''0\"E",
"latitude": "54°7'\''0\"N",
"sensors": []
}'
We got a Operation result response:
{
"success": true,
"message": null,
"data": {
"id": "7b5dab63-b9d9-4aac-dd19-08dcf42ec6b0",
"name": "Ufa meteo station",
"description": "Meteo station in Ufa city",
"longitude": "55°96'0\"E",
"latitude": "54°7'0\"N",
"sensors": null
}
}
Example of station creation postman (different from upper requests)
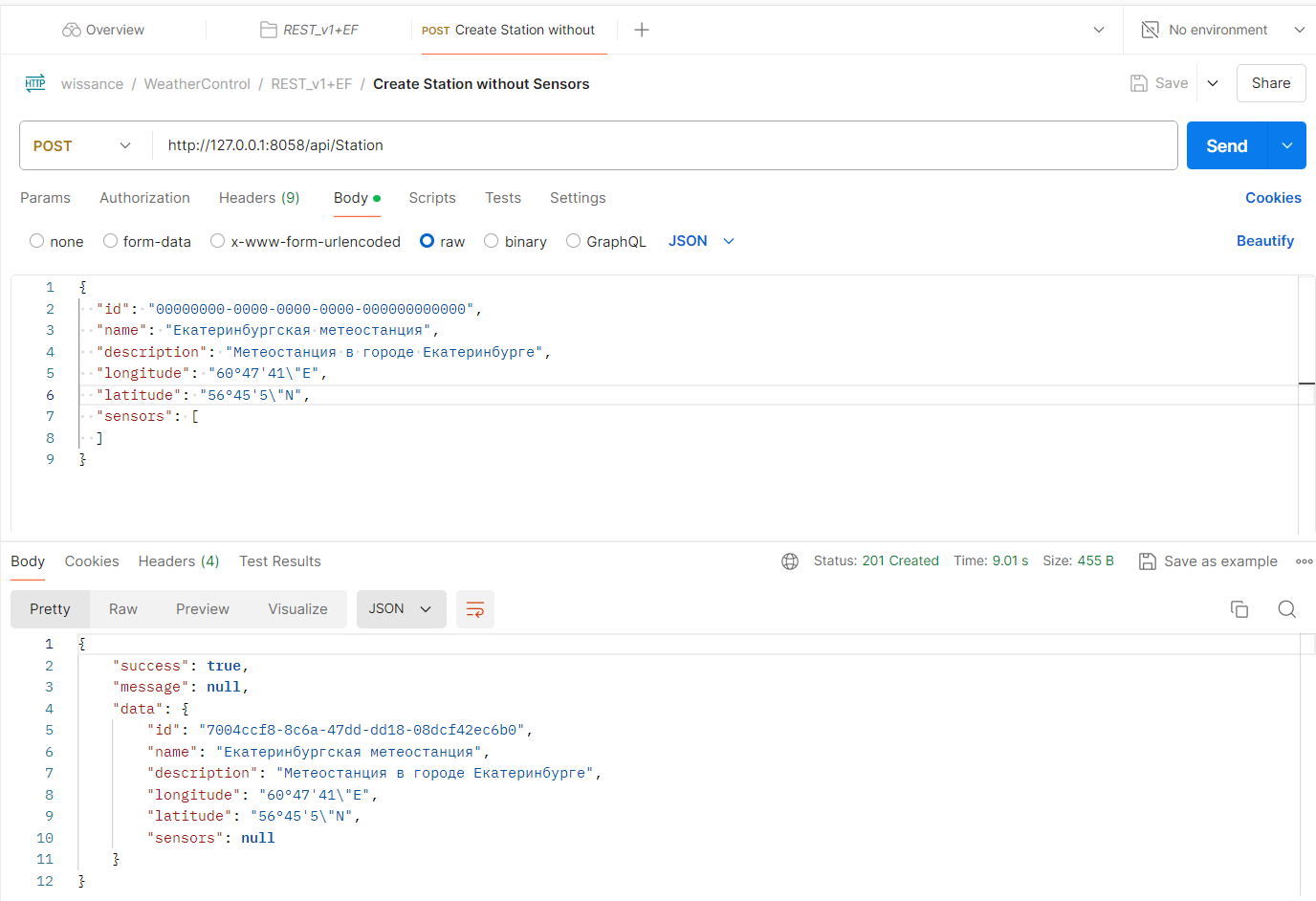
Example of station with sensors creation in postman (different from upper requests)
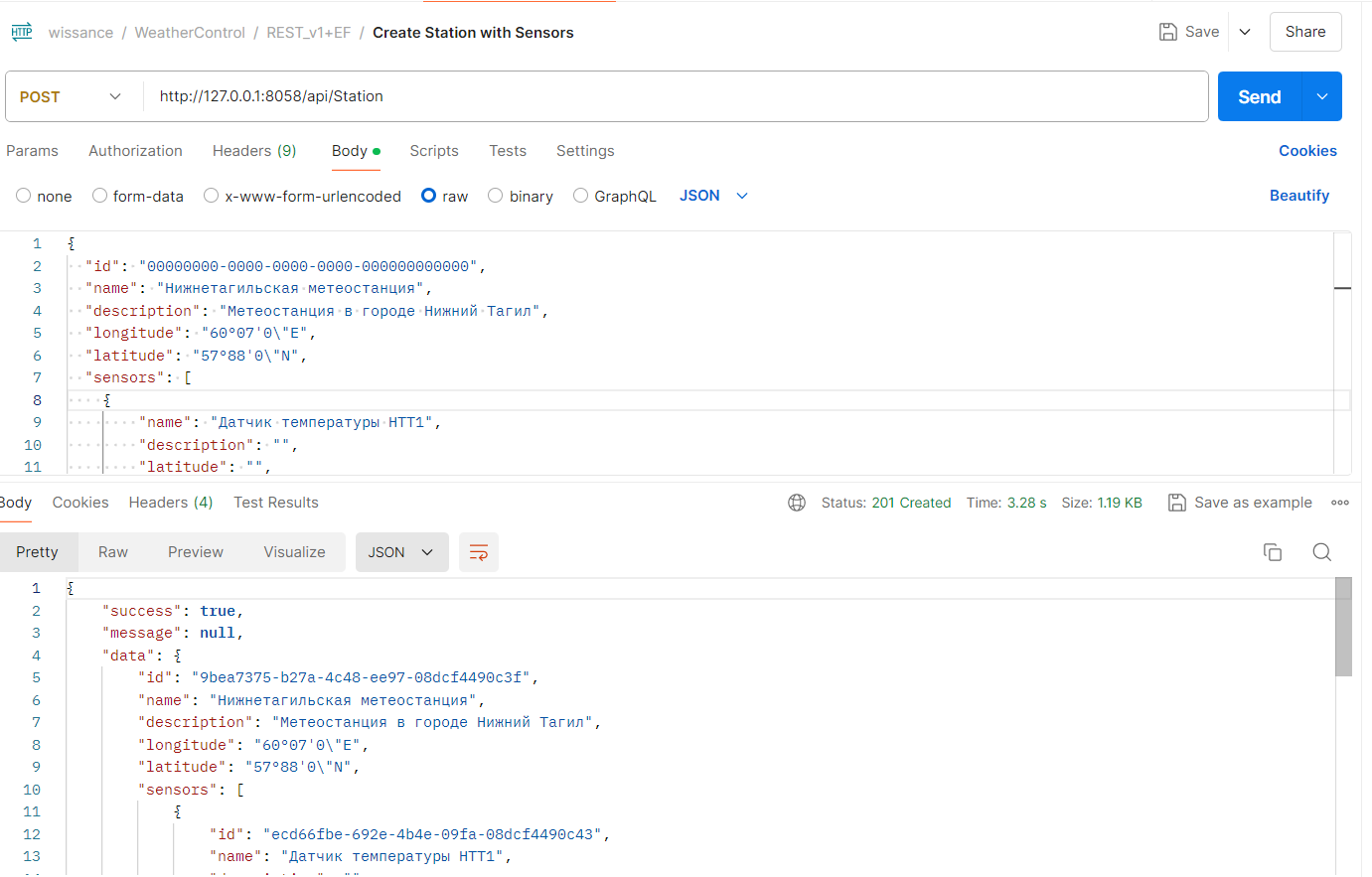
- Station data update (could be updated name, description and coordinates):
PUT http://localhost:8058/api/station/9bea7375-b27a-4c48-ee97-08dcf4490c3f
Body and response are the same as at Create operation, unlike Sensors are not editable through PUT:
{
"name": "Nizniy Tagil meteostation",
"description": "Nizniy Tagil meteostation (Sverdlovskaya region)",
"longitude": "60°07'0\"E",
"latitude": "57°88'0\"N",
"sensors": []
}
curl -X 'PUT' \
'http://127.0.0.1:8058/api/Station/9bea7375-b27a-4c48-ee97-08dcf4490c3f' \
-H 'accept: text/plain' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"name": "Nizniy Tagil meteostation",
"description": "Nizniy Tagil meteostation (Sverdlovskaya region)",
"longitude": "60°07'0\"E",
"latitude": "57°88'0\"N",
"sensors": []
}'
Example of running different station update in Postman:
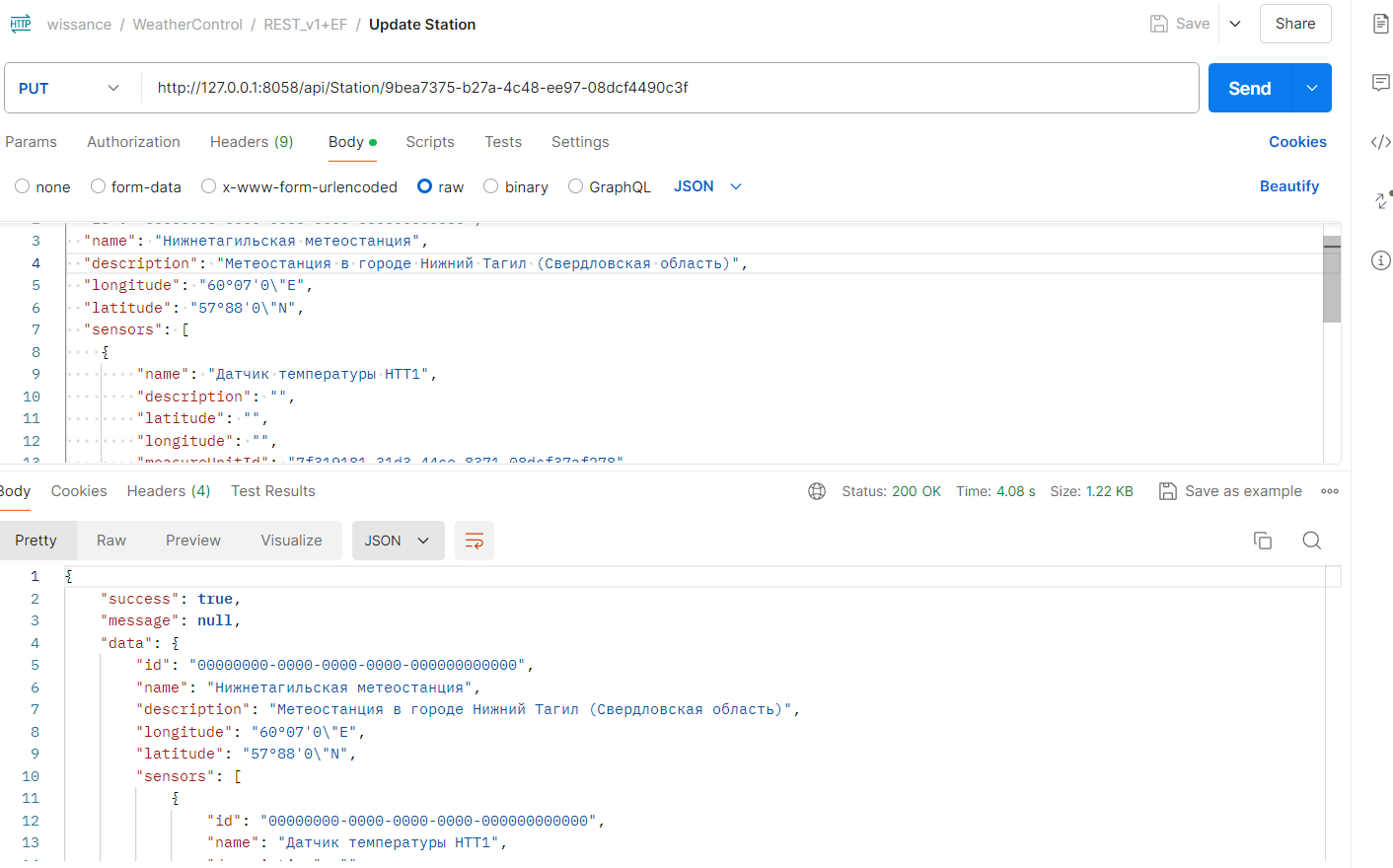
- There are two get endpoints:
- 3.1 to get
one by id-GET http://localhost:8058/api/station/{id} -
3.2 to get
collection with paging-GET http://localhost:8058/api/station/?page=1&size=10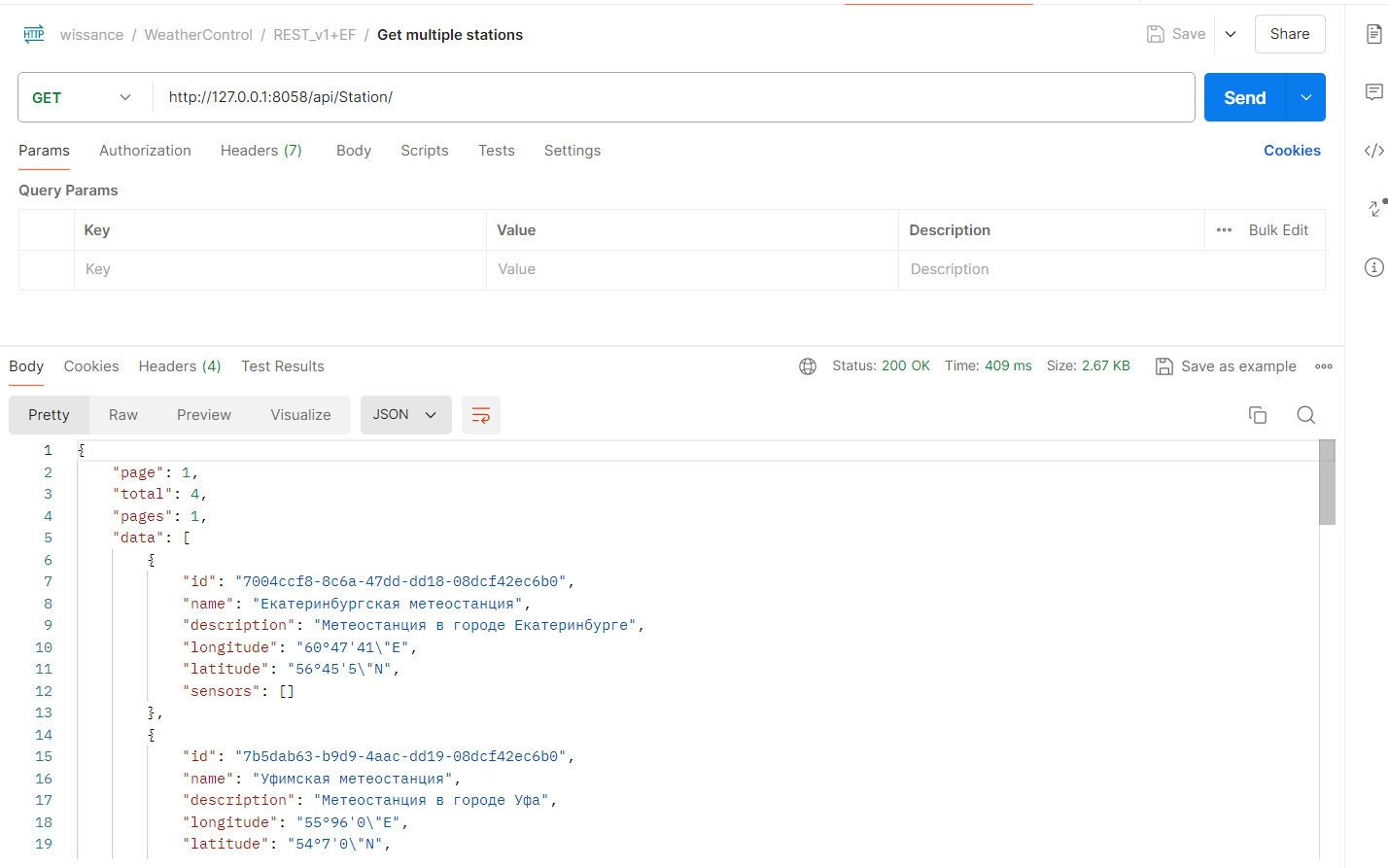
- To delete station with id
9bea7375-b27a-4c48-ee97-08dcf4490c3fuse endpointDELETE http://localhost:8058/api/station/9bea7375-b27a-4c48-ee97-08dcf4490c3f
3.2.4 Operations with Sensor resource
Operation with Sensors are the same as for Sensor.
- Create Sensor -
POST ~/api/Sensor, i.e.curl -X 'POST' \ 'http://127.0.0.1:8058/api/Sensor' \ -H 'accept: text/plain' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ -d '{ "name": "Temperature sensor ЕТ1", "description": "", "latitude": "", "longitude": "", "stationId": "7004ccf8-8c6a-47dd-dd18-08dcf42ec6b0", "measureUnitId": "7f319181-31d3-44ce-8371-08dcf37af278" }' - Update Sensor is similar to Create:
curl -X 'PUT' \ 'http://127.0.0.1:8058/api/Sensor/cb018a8a-cb03-4dbd-2b3c-08dcf466fe52' \ -H 'accept: text/plain' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ -d '{ "name": "Temperature sensor ЕТ1", "description": "Temperature sensor", "latitude": "", "longitude": "", "stationId": "7004ccf8-8c6a-47dd-dd18-08dcf42ec6b0", "measureUnitId": "7f319181-31d3-44ce-8371-08dcf37af278" }' - There are two get endpoints:
- 3.1 to get
one by id-GET http://localhost:8058/api/sensor/{id} - 3.2 to get
collection with paging-GET http://localhost:8058/api/station/?page=1&size=10with 2 additional params:- station (
Guid) for filtering Sensors by relation to station - mu (
Guid) for filtering Sensors by MeasureUnit
- station (
Examples of usage:
- Get multiple for MeasureUnit with id
7f319181-31d3-44ce-8371-08dcf37af278-http://127.0.0.1:8058/api/Sensor?mu=7f319181-31d3-44ce-8371-08dcf37af278 - Get multiple for MeasureUnit and Station
http://127.0.0.1:8058/api/Sensor?station=9694eacb-6470-46c2-dd1a-08dcf42ec6b0&mu=7f319181-31d3-44ce-8371-08dcf37af278
3.2.5 Operations with Measurement resource
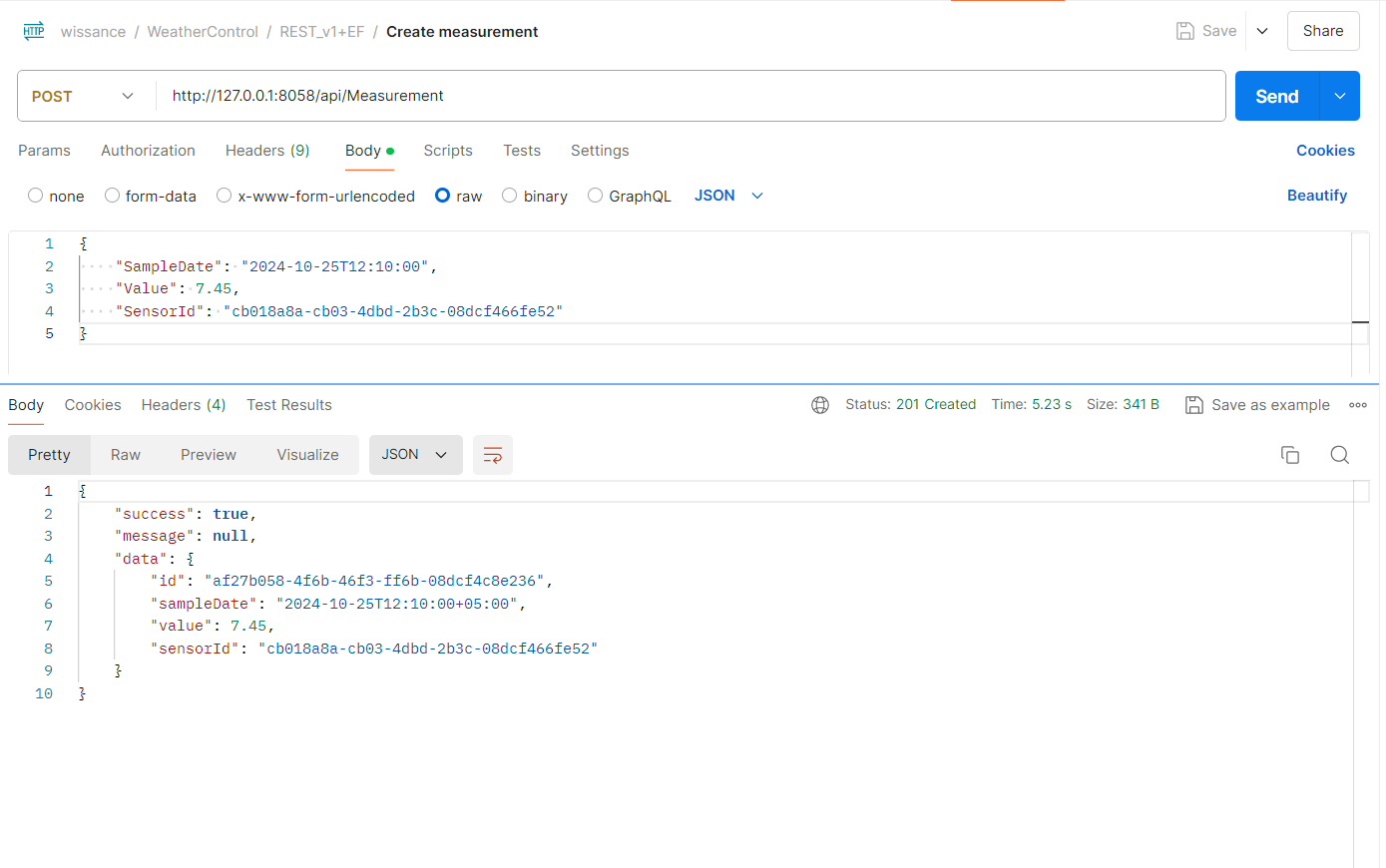
- Create measurements
POST http://localhost:8058/api/measurement
One measurement is one sample of measuring some MeasureUnit, Measurement directly relates to Sensor, not MeasureUnit (this could be discussed)
{
"SampleDate": "2024-10-25T12:10:00",
"Value": 7.45,
"SensorId": "cb018a8a-cb03-4dbd-2b3c-08dcf466fe52"
}
We got following result in the output:
{
"success": true,
"message": null,
"data": {
"id": "af27b058-4f6b-46f3-ff6b-08dcf4c8e236",
"sampleDate": "2024-10-25T12:10:00+05:00",
"value": 7.45,
"sensorId": "cb018a8a-cb03-4dbd-2b3c-08dcf466fe52"
}
}
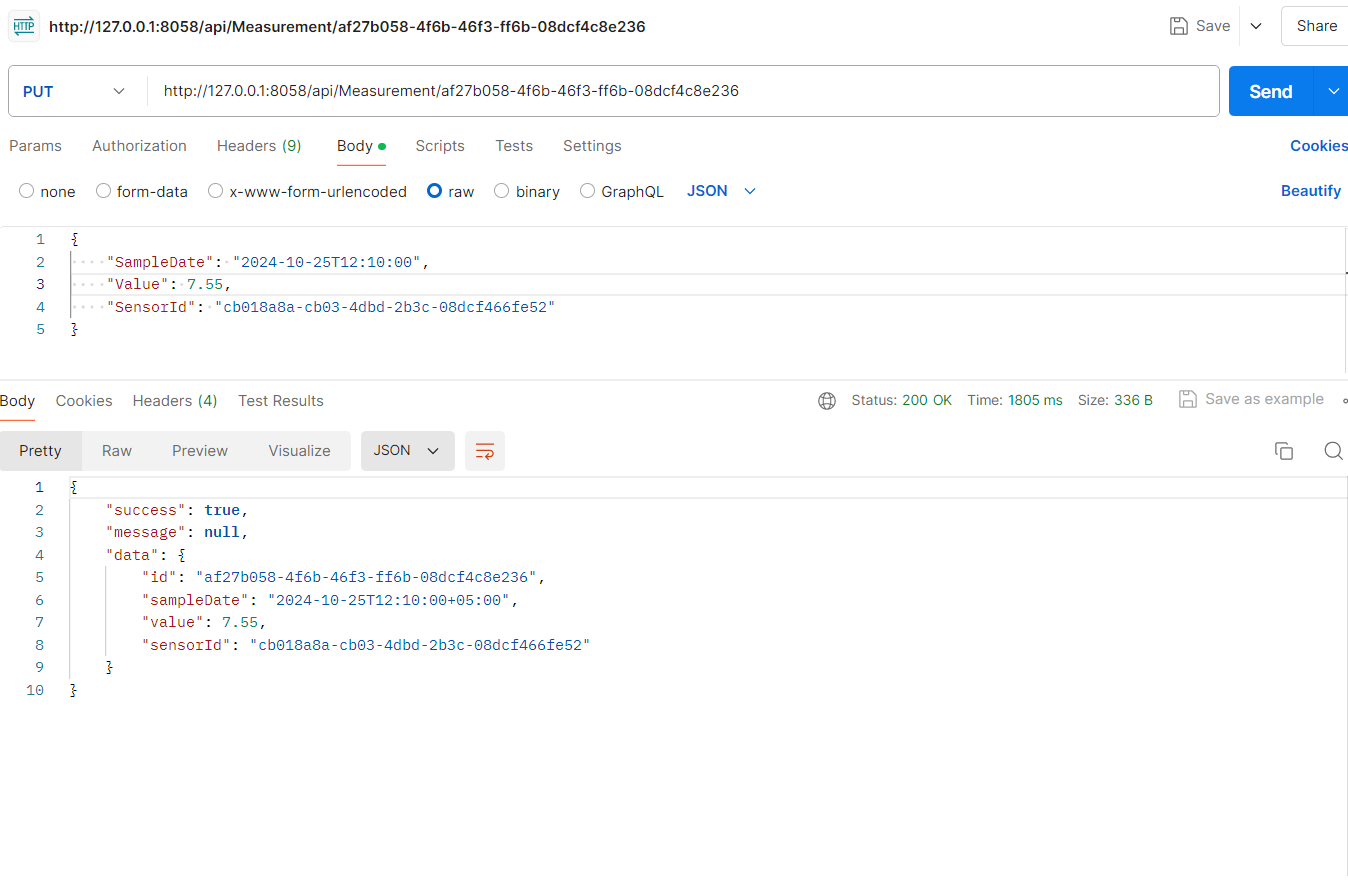
- Update measurements: one or any number of weather parameters could be changed using
PUT http://localhost:8058/api/measurements/af27b058-4f6b-46f3-ff6b-08dcf4c8e236with same body and result as at create measurements operation.
- There are two get operations:
- 3.1 to get one by id
GET http://localhost:8058/api/measurements/af27b058-4f6b-46f3-ff6b-08dcf4c8e236 - 3.2 to get collection with paging
GET http://localhost:8058/api/measurements/?page=1&size=10
- To delete measurements with id 1 use endpoint
DELETE http://localhost:8058/api/measurements/af27b058-4f6b-46f3-ff6b-08dcf4c8e236
4. REST API With EdgeDB
Here we’ve got a net6.0 REST Service that have the same model as previous service but persistent storage is EdgeDB not an SQL Server.
MeasureUnitMeasurementSensorStation
Model schema is here:
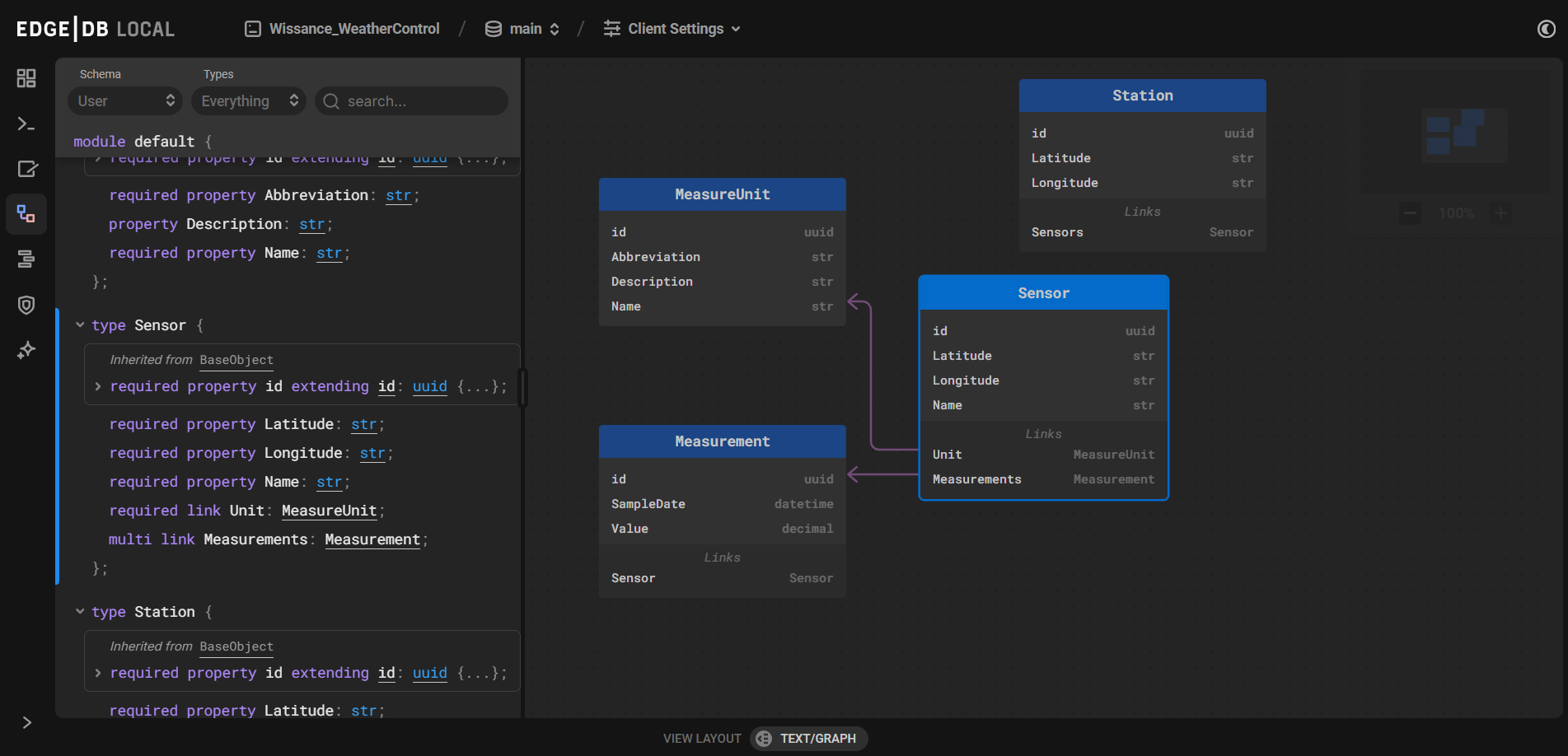
Data project is Wissance.WeatherControl.GraphData
4.1 Configure Edge DB (Prerequisites)
- Start
Edgedbinstance fromWissance.WeatherControl.GraphDatadirectory
edgedb instance start -I Wissance_WeatherControl --foreground
apply migration via
edgedb -I Wissance_WeatherControl migrate
- Configure Edgedb to allow pass own identifiers (necessary for object return after create)
edgedb -I Wissance_WeatherControl configure set allow_user_specified_id true
- Start edgedb ui:
edgedb ui
Once you loaded project you could use it in current application:
- Add proper Project Name in
appsettings.Development.jsonconfig file:"Application": { "Database": { "ProjectName": "Wissance_WeatherControl" } }
See how configuration works via project Name here
This package build connnection string using following scheme: edgedb://user:password@host:port/database
you could see your project credential on:
Windowsmachine in a directory:%USER_PROFILE%\AppData\Local\EdgeDB\config\credentialsLinuxmachine in a directory$HOME/.config/edgedb/credential
4.2 REST API With Edge DB
We are having following Key Items:
Controllers- we are using base classes from aWissance.WebApiToollit, in this lib we have either controllers for read-only and for fullCRUDresources.Managers- classes that are responsible for manage all business logic, in this project we have only one manager class -EdgeDbManagerthat is common forCRUDoperation over all resourcesEqlResolver- class that is responsible for associationmodel(resource) with operation (read,create,updateordelete)Factories- static classes that constructsDTOfromModelsand params (dictionary forcreateandupdateperform) fromDTO.
4.2.1 REST API Controllers
All controllers are located in a folder Controllers, just look how simply look full CRUD Controller:
namespace Wissance.WeatherControl.WebApi.V2.Controllers
{
public class MeasurementController : BasicCrudController<MeasurementDto, MeasurementEntity, Guid, , MeasureUnitFilterable>
{
public MeasurementController(EdgeDBClient edgeDbClient)
{
Manager = new EdgeDbManager<MeasurementDto, MeasurementEntity, Guid>(ModelType.Measurement, edgeDbClient,
MeasurementFactory.Create, MeasurementFactory.Create);
}
}
}
4.2.2 Manager
We have only one manager for all controllers due to the power of C# generics we just have to pass
to EdgeDbManager:
modelTypethat is using to find appropriate eql statements fromEqlResolverEdgeDbClientclient toedgedbdatabase- and 2 delegates that describes how to create representation (
DTO) from model and how to convertDTOto parameters list forinsertandupdateoperations
4.2.3 EqlResolver
Just a set of dictionaries every dictionary for one operation:
- get collection
- get one
- create
- update
- delete
4.2.4 Factories for objects transformation
They are static classes in a Factories directory, the looking quite simple:
namespace Wissance.WeatherControl.WebApi.V2.Factories
{
public static class SensorFactory
{
public static SensorDto Create(SensorEntity entity)
{
SensorDto dto = new SensorDto()
{
Id = entity.Id,
Name = entity.Name,
Latitude = entity.Latitude,
Longitude = entity.Longitude
};
if (entity.Measurements.Any())
{
dto.Measurements = entity.Measurements.Select(m => MeasurementFactory.Create((m))).ToList();
}
return dto;
}
public static IDictionary<string, object?> Create(SensorDto dto, bool generateId)
{
IDictionary<string, object?> dict = new Dictionary<string, object?>()
{
{"Name", dto.Name},
{"Latitude", dto.Latitude},
{"Longitude", dto.Longitude},
{"Measurements", dto.Measurements.Where(m => m.Id.HasValue)
.Select(m => m.Id.Value).ToArray()}
};
// TODO(this if for further getting created object)
dict["id"] = generateId ? Guid.NewGuid() : dto.Id;
return dict;
}
}
}